The Mind-Blowing Complications of Oral Infections: Brain Abscesses
By: Kevin Su
Introduction
After every dentist visit, you rarely leave without getting yet another memo to floss your teeth, and that is not without good reasons. Although tooth decay and gum diseases are the most common results of poor oral hygiene, oral infections can lead to serious complications. While most of the time we can’t prevent germs from entering our mouths, having poor dental hygiene allows unwanted microorganisms to flourish. But how bad can it get? What’s so concerning about stomach aches or an occasional tooth cavity? Well, in addition to food poisoning and other minor illnesses, mismanaged dental hygiene can result in the formation of brain abscesses.
What even are brain abscesses and do they form?
Brain abscesses, or cerebral abscesses, are localized infections that involve the accumulation of pus in vascular capsules within the brain. They occur when bacteria infiltrates the brain through entering the bloodstream, in many cases, from an oral infection. These abscesses usually form near the intersection of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes. According to data published on StatPearl in 2022, brain abscesses affect 1500~2500 people annually in the United States. Compared to brain tumors or intracranial masses, brain abscesses have a much lower incidence rate of 0.3~1.3 per 100,000. Though most oral infections do not lead to brain abscesses, people with right-to-left heart shunts, dental work in upper molars, compromised immunity, or poor dental hygiene are more at risk. Specifically, the shunts allow blood to bypass phagocytes (a type of white blood cells) and directly enter the brain. For this reason, people with those shunts are recommended to use antibacterial mouthwash or take antibiotics before any dental procedures.
How bad can brain abscesses get?
Symptoms range from headaches and fevers to neurological deficits and impaired consciousness, and the severity may depend on the location and size of the abscess. While the frequencies of each symptom vary across sources, headaches and fevers remain the most common effects of brain abscesses. In rare occasions, brain abscesses can lead to death, and has a mortality rate up to 53% under the worst circumstances.
How do we diagnose and treat brain abscesses?
Thanks to technological breakthroughs such as the invention of computerized tomography (CT), the mortality rate of brain abscesses has declined to 8~25% after 1970. With the help of CT and MRI, doctors can now confidently identify abscesses from other neurological diseases with similar symptoms. To identify the specific microorganism responsible for the abscess, doctors can perform gram staining, culture, histopathology, or even the newly developed “matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight” (MALDI-TOF). Altogether, these methods allow for more specific treatments for each case of brain abscess.
In addition to improved diagnosis using advanced imaging, evolution in antibiotic treatments also decreases the deadliness of these abscesses. For abscesses less than 1 cm in diameter, doctors can generally treat it using antibiotics without surgical interventions. As for abscesses larger than 1 cm, drainage is usually required before antibiotic treatments, either using a needle aspiration or an excision. The drainage is then used to identify the agent responsible for the abscess, allowing for more specific, targeted antibiotic treatments. Craniotomy is only required as a last resort for significantly larger, multi-lobulated abscesses that cause severe intracranial hypertension. After surgery, patients will go through antimicrobial treatment for six to eight weeks.
Conclusion
While most of us will never experience brain abscesses in our lives, this condition goes to show the importance of maintaining excellent dental hygiene. Even with modern technology, brain abscesses are still tricky to deal with and can still cause irreversible damage. But fear not, as oral infections are fairly easy to prevent as long as we stop dwelling in the comfort of our poor dental habits. Just follow your dentists’ advice on brushing and flossing, and don’t be afraid to ask them any questions about maintaining good dental hygiene. As the word goes, prevention is the best cure. Don’t be lazy about the only life you have!
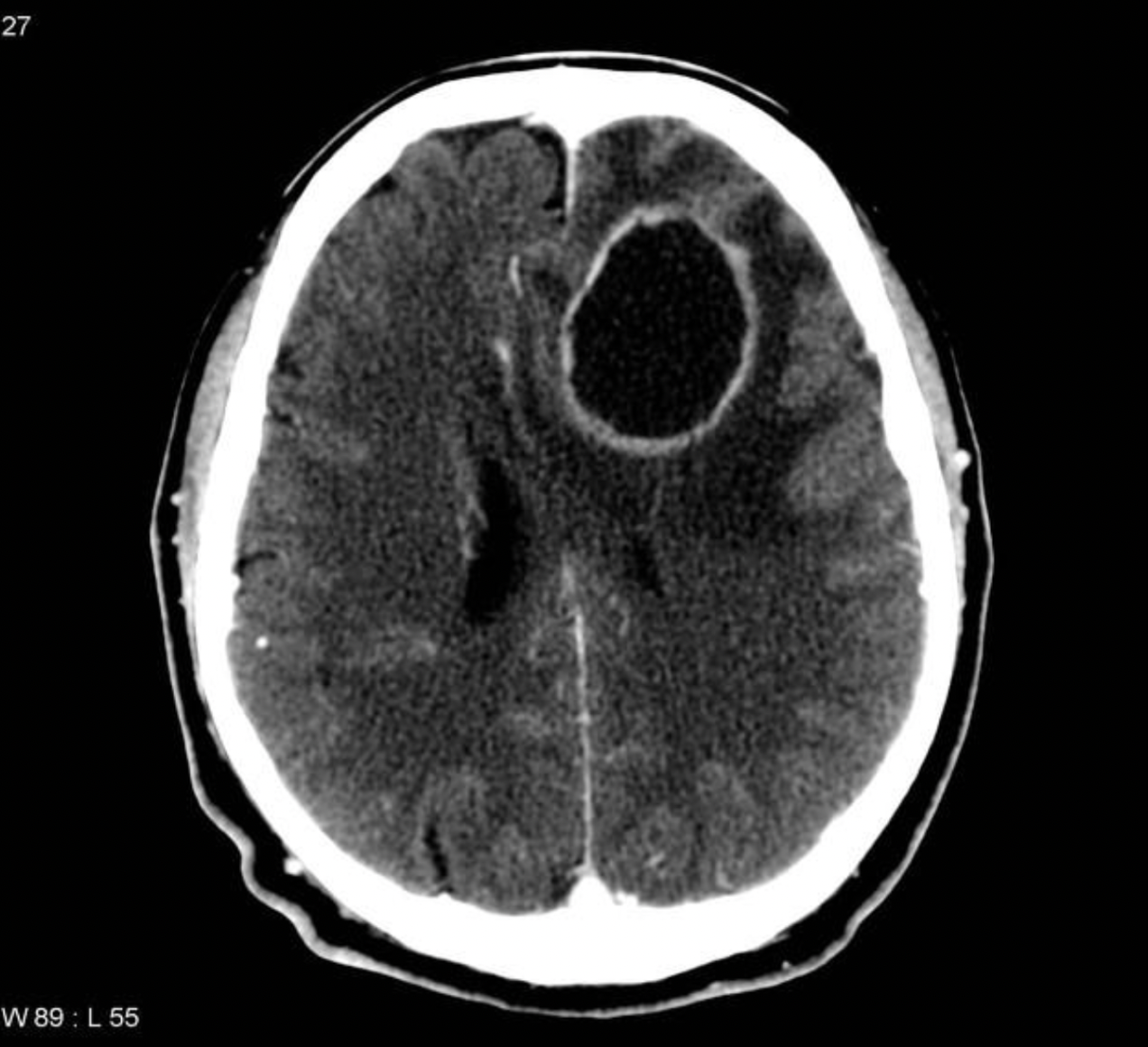
CT image of brain abscess in the frontotemporal region.
Pathophysiology of brain abscess in the case of congenital cyanosis heart disease. Here blood goes from the right ventricle into the left ventricle (following the green dashed path) instead of going into the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
Diagram of a brain abscess needle aspiration.
Four cross-section of a large human brain abscess in the temporal lobe.
References
Alvis-Miranda, H., Castellar-Leones, S. M., Elzain, M. A., & Moscote-Salazar, L. R. (2013). Brain abscess: Current management. Journal of neurosciences in rural practice, 4(Suppl 1), S67–S81. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-3147.116472.
Boatright, G. D., 2nd, Llerena, M. A., Gorelov, D. J., Alkaelani, M. T., Goeckeritz, J. R., & Lucke-Wold, B. (2022). Dental Infections and Risk for Brain Abscess: A Literature Review. Journal of dental and oral care, 1(1), https://www.mediresonline.org//article/dental-infections-and-risk-for-brain-abscess-a-literature-review.
Bokhari M.R., & Mesfin F.B. Brain Abscess. (2022, May 11). Brain Abscess. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441841/
Lumbiganon, P., & Chaikitpinyo, A. (2013). Antibiotics for brain abscesses in people with cyanotic congenital heart disease. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 2013(3), CD004469. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004469.pub3.
Rivera, K., Truckner, R., Furiato, A., & Martinez, S. (2021). The Diagnostic Challenge of the Pediatric Brain Abscess. Cureus, 13(6), e15402. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.15402.
Ruiz Barrera, M. A., Santamaria Rodriguez, A. F., & Zorro, O. F. (2022). Brain Abscess: A Narrative Review. Neurology Perspectives, 2(3) 160-167, https://www.elsevier.es/en-revista-neurology-perspectives-17-articulo-brain-abscess-a-narrative-review-S2667049622000291.